INSUBCONTINENT EXCLUSIVE:
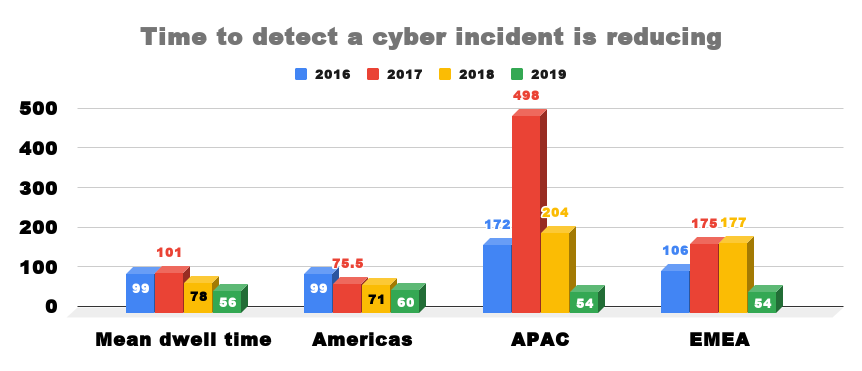
Organisations in Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA) are two days better than the global average of 56 days to detect a cyber incident as
organisations are detecting and containing attacks faster.In EMEA the median dwell time fell by 69.5% to 54 days in 2019 compared to 177
days in 2018.FireEye Mandiant M-Trends 2020 Report showed that organisations have put more emphasis on GDPR and increasing focus on security
due to the ongoing challenges organisations face from sophisticated threat actors.The global median dwell time decreased by 28% to 56 days
in 2019 compared to 78 days last year.Dwell time is calculated as the number of days an attacker is present in a victim network before they
The median represents a value at the midpoint of a data set sorted by magnitude.Internal detection, when an organisation independently
discovers that it has been compromised, fell 40.6% to 30 days compared to 50.5 days in 2018 while external notification, when an outside
entity informs an organisation that it has been compromised, also fell by 23.37% to 141 days compared to 184 days in 2018.For the first time
in four years, external notifications exceeded internal detections.FireEye Mandiant M-Trends 2020 Report showed that the shift is
potentially due to a variety of factors, such as increases in cybersecurity vendor and law enforcement notifications, the continued
expansion of the cybersecurity industry, changes in public disclosure norms and compliance changes.The report showed that over 500 new
malware families were observed in 2019, 58% of which were discovered through Mandiant service efforts, including incident responses.The
majority of these new samples either impacted Windows or multiple platforms while new malware families, solely impacting macOS and Linux,
remain in the minority.Furthermore, 70% of the samples identified belonged to one of the five most frequently seen families, which are based
on open source tools with active development
These points demonstrate that not only are malware authors innovating, cybercriminals are also outsourcing tasks to monetize operations
faster.Mandiant researchers analysed the 186 unique malware families from Mandiant engagements this year to reveal six traits and trends
Traits focus on the malware specifics, such as category, file type, accessibility and obfuscation
at which ransomware attacks can be carried out and the willingness of victims to pay, FireEye has assessed that threat groups will continue
to leverage ransomware as a secondary means for monetising their access to victim environments.The report revealed that the successful
has also led some established cybercrime groups to turn to ransomware as a secondary means of generating revenue
In 2019 we saw several cases in which threat actors that historically targeted sensitive information such as personally identifiable
FireEye Mandiant professionals responded to, the greatest majority (29%) were likely motivated by direct financial gain
This includes extortion, ransom, card theft, and illicit transfers
The second most common (22%) was data theft likely in support of intellectual property or espionage end goals.bQXHuL9FnWTzoidAbDo4YE.jpg?#